In today’s ever-evolving market, businesses face the constant challenge of optimizing pricing strategies to maximize revenue and maintain competitiveness. Dynamic pricing, also known as surge pricing, time-based pricing, or demand pricing, has emerged as a powerful tool to address this challenge. This approach allows businesses to adjust prices in real-time based on a variety of factors, including market demand, competitor pricing, and even external elements like weather or time of day. But is dynamic pricing the right strategy for your business? This article will explore the intricacies of dynamic pricing strategies, examining the potential benefits and drawbacks to help you determine if implementing dynamic pricing is suitable for your specific needs.
Implementing dynamic pricing can offer significant advantages, such as increased revenue generation, improved inventory management, and enhanced customer segmentation. However, it also presents potential risks, including customer alienation due to perceived unfairness, and the complexity of implementation and management. Understanding the nuances of different dynamic pricing strategies is crucial for successful execution. We’ll delve into the various types of dynamic pricing models, from cost-plus pricing and value-based pricing to segmented pricing and competitive pricing, providing you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about leveraging this potentially powerful pricing strategy within your own business context.
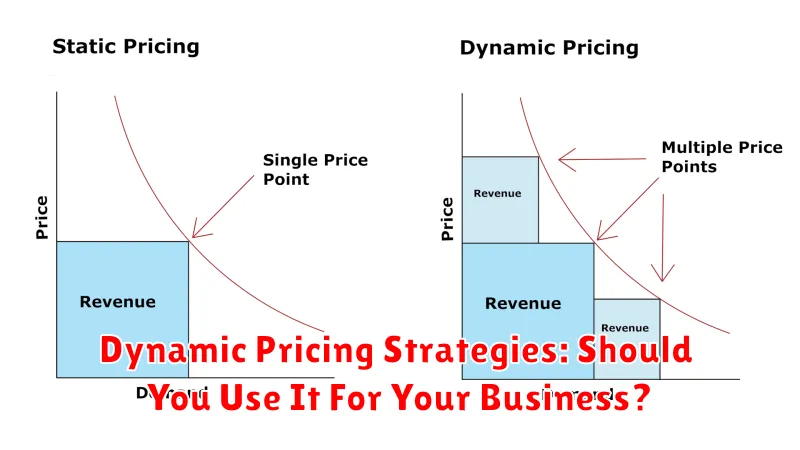
What is Dynamic Pricing?
Dynamic pricing, also known as surge pricing, time-based pricing, or demand pricing, is a pricing strategy where businesses set variable prices for products or services based on real-time market demand and other factors. This means prices can fluctuate, sometimes significantly, within a short period.
Instead of fixing a price and sticking to it, businesses using dynamic pricing adjust prices up or down to capture more revenue or market share. The key differentiator is the responsiveness of the pricing to current conditions.
A classic example of dynamic pricing is ride-sharing apps, where prices increase during periods of high demand, like rush hour or bad weather. However, dynamic pricing is applied across various industries, from airlines and hotels to e-commerce retailers and event ticketing platforms.
How Does Dynamic Pricing Work?
Dynamic pricing operates on the principle of adjusting prices in real-time based on various market factors. Algorithms are at the heart of this process, constantly analyzing data and making pricing decisions.
These algorithms consider factors like competitor pricing, demand fluctuations, and even external elements like weather patterns or time of day. For example, ride-sharing services often increase prices during peak hours due to higher demand.
Businesses set parameters and rules within the software, defining the upper and lower price limits. The algorithm then works within these predefined boundaries, ensuring prices remain within an acceptable range. This automated process eliminates the need for manual price changes and allows for quick reactions to market shifts.
Data feeds provide the algorithm with a continuous stream of information. This data is processed and analyzed to identify pricing trends and opportunities. Real-time adjustments are then made based on the programmed logic and market conditions.
Benefits of Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing, when implemented effectively, can offer several advantages for businesses. A primary benefit is increased revenue. By adjusting prices to reflect real-time demand, businesses can capture higher profits during peak periods. This also allows for optimized pricing during slower periods to stimulate sales and avoid lost revenue.
Improved competitiveness is another key advantage. Dynamic pricing enables businesses to react quickly to competitor price changes and maintain a competitive edge in the market. This flexibility allows for nimble responses to market fluctuations.
Enhanced customer segmentation can also be achieved through dynamic pricing. Businesses can tailor pricing to different customer segments based on their purchasing behavior, demographics, or other factors. This allows for personalized pricing strategies that cater to specific customer groups.
Finally, dynamic pricing provides valuable data insights. By tracking price changes and their impact on sales, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of customer price sensitivity and demand elasticity. This data-driven approach allows for continuous optimization of pricing strategies.
Drawbacks of Dynamic Pricing
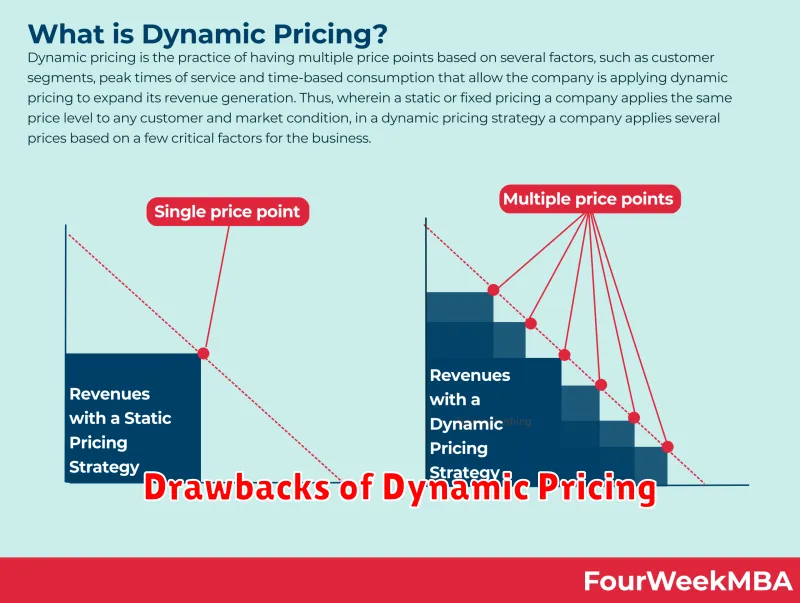
While dynamic pricing offers several advantages, businesses must also consider potential downsides before implementation. A primary concern is customer alienation. Frequent price fluctuations can erode customer trust and loyalty, particularly if perceived as unfair or manipulative. This is especially true for businesses with established customer bases who expect consistent pricing.
Price wars are another potential drawback. In highly competitive markets, dynamic pricing can trigger retaliatory price adjustments from competitors, leading to a race to the bottom and diminished profit margins for all involved. Complexity is also a factor. Implementing and managing a dynamic pricing system requires sophisticated software and analytical capabilities, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Finally, there is the risk of legal and ethical issues. While generally acceptable, dynamic pricing can attract scrutiny if perceived as price gouging or discriminatory, particularly during periods of high demand or emergencies. Businesses must carefully consider these potential drawbacks and implement strategies to mitigate negative impacts.
Different Dynamic Pricing Strategies
Several dynamic pricing strategies exist, each designed to achieve specific business goals. Choosing the right one depends on your industry, market conditions, and overall objectives.
Cost-Plus Pricing
This strategy involves adding a fixed markup to the cost of goods or services. While simple, it doesn’t account for market fluctuations or competitor pricing.
Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing focuses on the perceived value of a product or service to the customer. This strategy can be effective for premium products or services where customers are willing to pay more for perceived quality.
Competitive Pricing
This strategy involves closely monitoring and adjusting prices based on competitor pricing. It can be effective in highly competitive markets but risks triggering price wars.
Segmented Pricing
Segmented pricing involves charging different prices to different customer segments based on factors like demographics, purchase history, or location.
Time-Based Pricing
This strategy involves adjusting prices based on time, such as day of the week, time of day, or season. This is common in industries like travel and hospitality.
When to Use (and Not Use) Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing, while powerful, isn’t suitable for every business. Understanding the optimal scenarios for its implementation is crucial for maximizing its benefits and avoiding potential pitfalls.
When to Use Dynamic Pricing:
Consider dynamic pricing if your business experiences fluctuating demand, offers perishable goods or services, operates in a highly competitive market, or has a large inventory that needs to be managed efficiently. Industries like travel, hospitality, and event ticketing often benefit from this strategy.
When Not to Use Dynamic Pricing:
Avoid dynamic pricing if your business prioritizes price transparency and customer loyalty above all else. Frequent price changes can erode trust and alienate customers, especially in markets with low price sensitivity. Businesses selling essential goods or those with a strong brand identity built on consistent pricing should generally steer clear of dynamic pricing.
Furthermore, if you lack the technical infrastructure or the data analysis capabilities to implement dynamic pricing effectively, it’s best to avoid it. Poorly executed dynamic pricing can lead to lost revenue and customer dissatisfaction.
Implementing Dynamic Pricing in Your Business
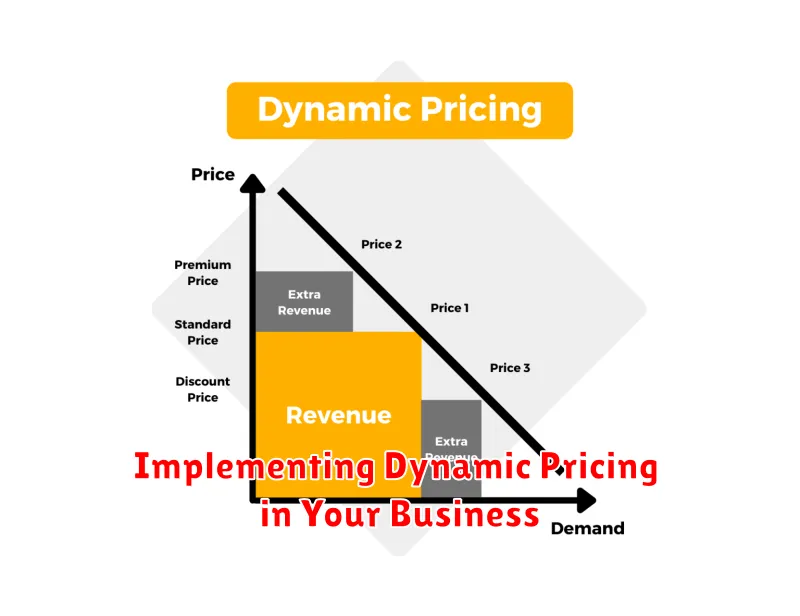
Implementing dynamic pricing requires a strategic approach. Begin by clearly defining your objectives. Are you aiming to maximize revenue, increase market share, or perhaps optimize inventory management? This clarity will guide your pricing strategy.
Next, segment your market. Identify distinct customer groups with varying price sensitivities. This segmentation allows for tailored pricing strategies that resonate with each group.
Invest in the right technology. A robust pricing platform is essential. This software should integrate with your existing systems, automate price adjustments, and provide real-time data analysis. Consider factors like competitor pricing, demand fluctuations, and available inventory when choosing a platform.
Test and refine your approach. Start with a small-scale implementation to gather data and identify potential challenges. Continuously analyze the results and adjust your strategy accordingly to optimize performance.
Best Practices for Successful Dynamic Pricing
Implementing dynamic pricing successfully requires careful planning and execution. Transparency is paramount. Clearly communicate pricing adjustments to customers to build trust and avoid alienating them. Explain the rationale behind changes, highlighting factors like demand or competitor pricing.
Data analysis is crucial. Continuously monitor sales data, competitor prices, and market trends to inform pricing decisions. Utilize A/B testing to optimize pricing strategies and understand customer responses to different price points. Establish clear pricing floors and ceilings to prevent extreme price fluctuations that could damage brand perception.
Segmentation is key. Group customers based on their purchasing behavior, demographics, or other relevant factors. This allows for targeted pricing adjustments that cater to specific segments’ price sensitivities. Regularly review and refine your dynamic pricing model. Market conditions change, and your pricing strategy should adapt accordingly.
Measuring the Success of Your Dynamic Pricing Strategy
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of your dynamic pricing strategy. Regular monitoring allows for necessary adjustments and optimizations. Don’t just set it and forget it!
Track revenue growth. Is your overall revenue increasing since implementation? Compare current revenue with pre-dynamic pricing figures. A positive trend suggests the strategy is working. However, ensure this growth isn’t coming at the expense of customer satisfaction.
Monitor your conversion rates. Are more customers completing purchases? Dynamic pricing can sometimes deter customers if not implemented correctly. A dip in conversions might signify a need to revise your pricing rules.
Analyze profit margins. While revenue might increase, are you maintaining profitability? Calculate profit margins regularly to ensure the pricing strategy isn’t eroding your bottom line. Balancing revenue and profit is key.
Assess competitor pricing. How do your dynamically adjusted prices compare with the competition? Consistent monitoring helps you stay competitive while maximizing revenue and profit. Remember, the market is constantly evolving.