In today’s digital landscape, a robust online presence is crucial for business success. For e-commerce businesses, this translates to having a seamless and secure payment process. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of e-commerce payment gateways, providing online businesses with the knowledge they need to choose the right solution for their needs. Understanding how payment gateways work is essential for accepting online payments, managing transactions, and ensuring a positive customer experience. This guide will decode the complexities of online payment processing, covering key aspects such as security, functionality, and integration.
From credit card processing and mobile payments to alternative payment methods, this guide explores the various options available to online businesses. We’ll examine the benefits of using a payment gateway, discuss the different types of payment gateways, and provide insights into choosing the best payment gateway for your specific business model. Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, understanding the nuances of e-commerce payment solutions is paramount to driving sales and fostering customer trust. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of digital payments and optimize your online payment strategy.
What is an E-commerce Payment Gateway?
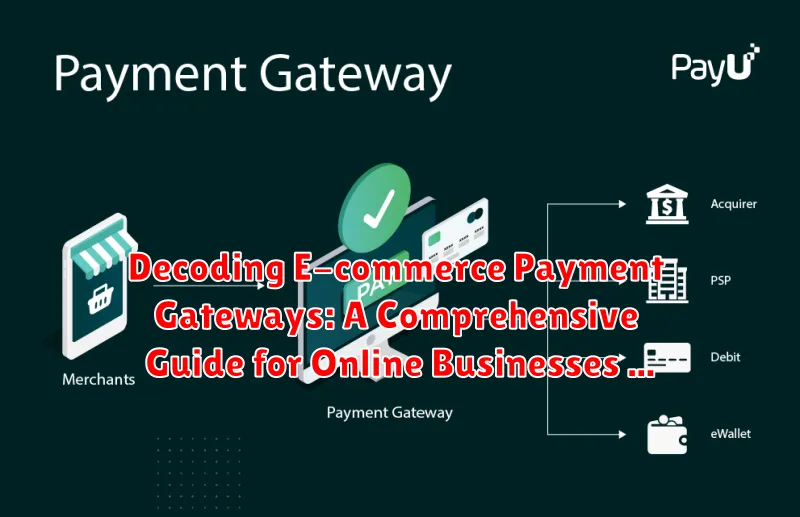
In the simplest terms, an e-commerce payment gateway is a technology that facilitates the transfer of funds between a customer and an online merchant. Think of it as the digital equivalent of a physical point-of-sale (POS) terminal you see in brick-and-mortar stores. It securely authorizes payments for online purchases, ensuring the smooth flow of transactions.
When a customer completes an online purchase, the payment gateway steps in to process the transaction. It encrypts sensitive payment information, such as credit card details, and transmits it securely to the payment processor.
The payment gateway acts as a critical intermediary, connecting your online store to the wider financial network. It plays a vital role in protecting both the buyer and the seller from fraud by verifying the legitimacy of the transaction.
How Payment Gateways Work: A Step-by-Step Explanation
Understanding how payment gateways function is crucial for any online business. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
Step 1: Customer Initiates Payment: The customer selects their desired products and proceeds to checkout, entering their payment information.
Step 2: Encryption and Transmission: The payment gateway encrypts the sensitive data and securely transmits it to the payment processor.
Step 3: Authorization Request: The payment processor sends an authorization request to the customer’s issuing bank.
Step 4: Authorization Response: The issuing bank verifies the funds and sends back an authorization response (approved or declined).
Step 5: Settlement: If approved, the payment gateway captures the funds and initiates the settlement process, transferring the money to the merchant’s account.
Step 6: Confirmation: The customer and the merchant receive confirmation of the successful transaction.
Types of Payment Gateways Available for Online Stores
Understanding the different types of payment gateways is crucial for selecting the best fit for your business. Broadly, payment gateways can be categorized into three main types:
1. Redirected Payment Gateways
These gateways redirect customers to a third-party payment page to complete their transaction. While simple to implement, this method can sometimes impact the customer experience due to the shift away from your website.
2. Direct Post Payment Gateways
With direct post gateways, customers enter their payment information directly on your website, and the gateway securely transmits the data for processing. This method offers a more seamless checkout experience.
3. Hosted Payment Gateways
Hosted gateways combine elements of both redirected and direct post methods. The payment form is hosted by the gateway provider, but it can be customized to match your website’s branding, offering a balance of security and user experience.
Choosing the right type depends on factors like your business size, transaction volume, and desired level of checkout customization.
Key Features to Look for in a Payment Gateway
Selecting the right payment gateway is crucial for a smooth and secure checkout experience. Several key features should be considered during the selection process.
Security is paramount. Look for gateways offering robust fraud prevention tools, including address verification, CVV checks, and 3D Secure authentication. PCI DSS compliance is non-negotiable, ensuring the gateway adheres to strict security standards for handling sensitive cardholder data.
Supported Payment Methods are another critical factor. The gateway should support a range of payment options relevant to your target audience, including major credit and debit cards, digital wallets, and potentially even alternative payment methods like buy now, pay later. Consider your customer base and their preferred payment preferences.
Transaction Fees and other costs associated with the gateway should be transparent and competitive. Evaluate different pricing models, including per-transaction fees, monthly fees, and setup costs, to determine the most cost-effective option for your business.
Integration with your existing e-commerce platform should be seamless. Ensure compatibility and look for gateways that offer easy integration with your chosen platform or shopping cart.
Finally, consider the customer support offered by the payment gateway provider. Reliable and accessible technical support can be invaluable in troubleshooting any issues that may arise.
Choosing the Right Payment Gateway for Your Business Needs
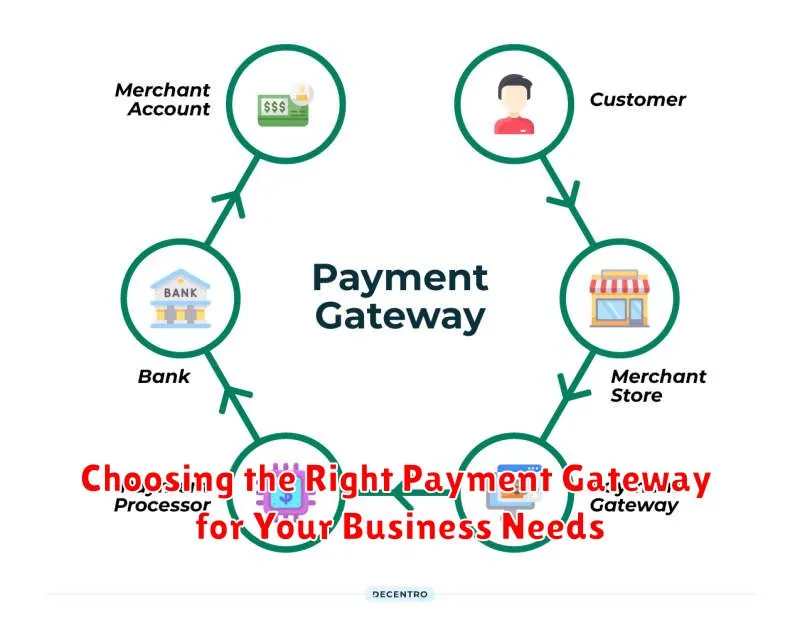
Selecting the right payment gateway is crucial for a smooth and secure checkout experience. Several factors influence this decision, aligning with your specific business requirements.
Transaction Volume: High-volume businesses benefit from gateways offering lower per-transaction fees, while low-volume businesses might prioritize gateways with minimal monthly fees.
Business Type and Location: Consider whether you operate internationally or domestically. Some gateways specialize in cross-border transactions and multi-currency support. Local regulations and compliance requirements also influence your choice.
Integration with Existing Platforms: Ensure the gateway seamlessly integrates with your e-commerce platform and other business tools. A smooth integration minimizes technical complexities and streamlines operations.
Security Features: Prioritize security features like fraud detection, PCI DSS compliance, and data encryption to protect your business and customer data.
Customer Support: Reliable customer support is essential for addressing any technical or transactional issues promptly. Evaluate the gateway’s support channels and availability.
Integrating a Payment Gateway with Your E-commerce Platform
Integrating a payment gateway is crucial for accepting online payments. The process typically involves selecting a compatible gateway and following its integration documentation. Your e-commerce platform might offer pre-built integrations simplifying the process.
Generally, integration involves exchanging API keys and secret tokens between your platform and the gateway. Testing transactions in a sandbox environment is essential before going live. This allows you to verify the setup and ensure seamless payment processing without risking real financial transactions.
Key considerations include supported payment methods and currencies. Ensure the gateway aligns with your target market’s preferred payment options. Additionally, understand the technical requirements and any necessary coding adjustments for your platform.
Security Measures and PCI Compliance for Payment Gateways
Security is paramount when processing online payments. Payment gateways employ various measures to protect sensitive data. Encryption scrambles information transmitted between the customer, merchant, and payment processor, rendering it unreadable to unauthorized parties. Tokenization replaces sensitive card details with unique tokens, reducing the risk of data breaches. Fraud detection tools monitor transactions for suspicious activity and flag potentially fraudulent payments.
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliance is mandatory for all businesses that handle cardholder data. This standard outlines a set of security requirements designed to protect cardholder information and minimize the risk of fraud. Compliance involves implementing strong security measures, regularly testing systems, and maintaining a secure network.
Key PCI DSS requirements include building and maintaining a secure network, protecting cardholder data, maintaining a vulnerability management program, implementing strong access control measures, regularly monitoring and testing networks, and maintaining an information security policy.
Understanding Payment Gateway Fees and Charges
Navigating the costs associated with payment gateways is crucial for effective budget management. Understanding the various fee structures will help you optimize your pricing strategy and ultimately, your profitability.
Most payment gateways employ a combination of fees, including transaction fees, which are charged per transaction processed. These are often a percentage of the transaction amount plus a fixed fee. Monthly fees are common and cover the gateway’s ongoing services. Some gateways also charge setup fees for initial integration and account configuration.
Chargeback fees are applied when a customer disputes a charge, and refund processing fees can also be incurred. It’s important to be aware of these potential charges and factor them into your financial projections.
Different payment gateways have different pricing models. Some offer tiered pricing, where fees decrease with higher transaction volumes. Others utilize interchange-plus pricing, a more transparent model that passes the interchange fees directly to the merchant, plus a markup from the gateway.
Troubleshooting Common Payment Gateway Issues
Encountering payment gateway issues can be frustrating for both businesses and customers. Swiftly resolving these problems is crucial for maintaining a smooth checkout process and preserving customer trust.
Common issues include declined transactions, connection errors, and authorization failures. Declined transactions often stem from insufficient funds, incorrect card details, or security flags raised by the issuing bank. Addressing this requires verifying customer information and suggesting alternative payment methods.
Connection errors can arise from server downtime, network connectivity problems, or incorrect gateway configuration. Checking server status, network connections, and API settings can help pinpoint the source of the issue.
Authorization failures typically occur when the issuing bank refuses to authorize the transaction. Reasons can range from suspected fraud to exceeding credit limits. Contacting the customer and the payment gateway provider can provide further insights.
Maintaining detailed logs of transactions and errors is essential for efficient troubleshooting. These logs aid in identifying patterns and resolving recurring issues.
The Future of Payment Gateways: Emerging Trends

The landscape of e-commerce payment gateways is constantly evolving. Several key trends are shaping the future of online transactions, promising greater speed, security, and flexibility for both businesses and consumers.
Invisible Payments are gaining traction, aiming to create a seamless checkout experience. By integrating payment details behind the scenes, customers can complete purchases with minimal interaction, reducing cart abandonment.
Biometric Authentication is enhancing security by utilizing fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and other biological markers to verify customer identity. This adds an extra layer of protection against fraud.
The rise of Mobile Wallets continues to reshape payment processing. With increasing adoption rates, digital wallets offer streamlined checkout processes on mobile devices, contributing to the growth of m-commerce.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is being implemented to improve fraud detection and risk management. AI-powered systems can analyze transaction data in real-time, identifying suspicious patterns and preventing fraudulent activities.