In today’s digital age, payment processors are essential for businesses of all sizes. Understanding how payment processing works is crucial for accepting payments smoothly and efficiently. This article will delve into the intricacies of payment gateways, merchant accounts, and the overall payment processing ecosystem, explaining their functions and importance for your business’s success. Whether you’re running an e-commerce store, a brick-and-mortar shop, or a subscription-based service, understanding payment processors is fundamental to secure and reliable transactions.
From credit card processing to online payment solutions, navigating the world of payment processors can feel overwhelming. This comprehensive guide will break down the key components of the payment process, outlining the roles of different parties involved, including the merchant, the customer, the issuing bank, and the acquiring bank. We will also explore the various types of payment methods available, highlighting the benefits and considerations for each, empowering you to choose the optimal payment processing solution for your specific business needs.
What is a Payment Processor?
A payment processor is a company that acts as the intermediary between a merchant and financial institutions to facilitate electronic payments. They enable businesses to accept various payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, and other digital payment options, both online and in person. Think of them as the essential bridge connecting your business to the complex world of financial networks.
In essence, a payment processor handles the entire transaction process from authorization and settlement to funding the merchant’s account. They ensure the secure and efficient transfer of funds, while also managing the various security protocols and regulations involved in processing payments.
Payment processors play a crucial role in modern commerce by streamlining transactions, reducing the complexities of managing multiple payment systems, and offering businesses the ability to accept a wider range of payment options, ultimately expanding their reach and potential customer base.
How Payment Processors Work: A Step-by-Step Guide
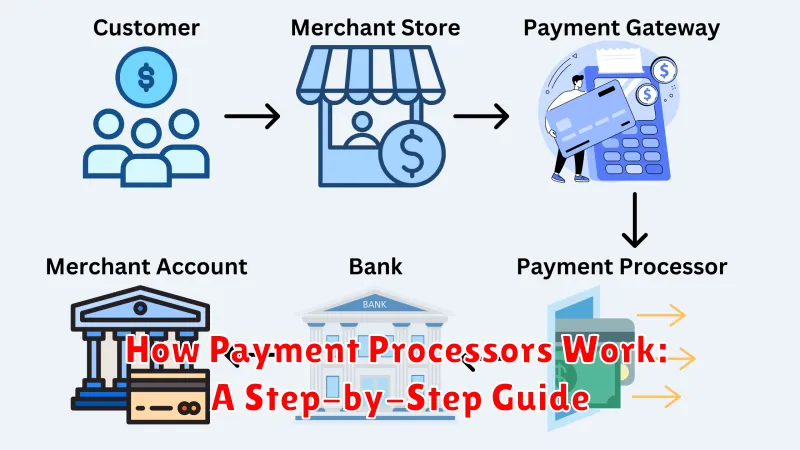
Understanding how payment processors function is crucial for any business accepting online payments. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
-
Initiation: The process begins when a customer decides to purchase a product or service and proceeds to checkout.
-
Payment Information Submission: The customer enters their payment details, such as credit card number, expiration date, and CVV code, on the merchant’s website or app. This information is encrypted for security.
-
Payment Gateway: The encrypted payment information is then securely transmitted to the payment gateway. The payment gateway acts as a secure bridge between the merchant and the payment processor.
-
Payment Processor: The payment processor receives the encrypted data from the gateway and communicates with the relevant card networks (e.g., Visa, Mastercard, American Express). It requests authorization for the transaction.
-
Authorization Request: The card network verifies the customer’s account details with the issuing bank to ensure sufficient funds and validity.
-
Authorization Response: The issuing bank either approves or declines the transaction. This response is relayed back to the payment processor.
-
Merchant Notification: The payment processor informs the merchant and the customer of the authorization status. If approved, the funds are earmarked for the merchant.
-
Settlement: Finally, the payment processor facilitates the transfer of funds from the customer’s bank account to the merchant’s account, completing the transaction.
Types of Payment Processors: Merchant Accounts vs. Payment Service Providers
Businesses typically choose between two main types of payment processors: merchant accounts and payment service providers (PSPs). Understanding the differences is crucial for selecting the right solution.
Merchant accounts are dedicated bank accounts specifically for processing credit and debit card payments. They offer more control over transaction fees and processing but require an application process and often involve more setup.
Payment service providers (PSPs) aggregate transactions from multiple businesses under a single merchant account. This simplifies the setup process, as there’s no individual merchant account application required. However, businesses typically have less control over fees and may face stricter processing regulations.
Choosing the right type depends on your business needs. Larger businesses with high transaction volumes may benefit from the lower processing fees and greater control offered by a merchant account. Smaller businesses or startups may find the ease of use and quick setup of a PSP more appealing.
Key Features to Look for in a Payment Processor
Choosing the right payment processor is crucial for your business. Consider these key features when evaluating your options:
Security
Security is paramount. Look for processors compliant with PCI DSS standards, offering features like fraud detection, tokenization, and encryption to protect sensitive customer data.
Pricing and Fees
Understand the fee structure. This includes transaction fees, monthly fees, chargeback fees, and any other potential costs. Compare different processors to find the most cost-effective solution for your business model.
Accepted Payment Methods
Ensure the processor supports the payment methods your customers prefer. This may include credit and debit cards, digital wallets (like Apple Pay or Google Pay), and other options relevant to your target market.
Integration and Compatibility
Seamless integration with your existing website and other business software is essential. Check for compatibility with your e-commerce platform, accounting software, and other tools.
Customer Support
Reliable customer support is crucial for troubleshooting any issues that may arise. Look for processors that offer responsive support via phone, email, or chat.
Benefits of Using a Payment Processor for Your Business
Integrating a payment processor offers numerous advantages that can significantly impact your business’s growth and operational efficiency. By facilitating seamless transactions, payment processors contribute to increased sales and improved cash flow.
Improved Security: Payment processors adhere to strict security standards, reducing the risk of fraud and data breaches, safeguarding both your business and your customers’ sensitive information. This enhanced security builds trust and encourages customer confidence.
Increased Sales: Offering a variety of payment options caters to a wider customer base, including those who prefer credit cards, debit cards, or digital wallets. This convenience can lead to higher conversion rates and increased sales.
Enhanced Efficiency: Automating payment processing streamlines administrative tasks, reduces manual errors, and frees up valuable time and resources for other essential business operations.
Faster Payments: Payment processors expedite transaction processing, ensuring quick access to funds, improving cash flow management, and facilitating smoother business operations.
Choosing the Right Payment Processor for Your E-commerce Store
Selecting the right payment processor is crucial for the success of your online business. Several factors should influence your decision. Transaction fees are a primary concern, varying by processor and transaction type. Consider whether you’ll be processing primarily credit cards, debit cards, or alternative payment methods like digital wallets.
Your target audience also plays a role. If you operate internationally, ensure the processor supports currencies and payment methods common in your target markets. Security is paramount; choose a processor compliant with PCI DSS standards to protect your customers’ sensitive data.
Think about your business model and sales volume. Some processors cater to small businesses, while others specialize in high-volume transactions. Finally, consider the integration process. Look for a processor that seamlessly integrates with your existing e-commerce platform.
Integrating a Payment Processor with Your Website
Integrating a payment processor is crucial for accepting online payments. There are two primary integration methods: using a payment gateway or a payment aggregator.
Payment Gateway Integration
Gateways act as a secure bridge between your website and the payment processor. Customer payment information is securely transmitted to the gateway, then to the processor, and finally to the acquiring bank. This method generally requires more technical expertise and may involve setting up a merchant account.
Payment Aggregator Integration
Aggregators simplify integration by allowing you to process payments without a dedicated merchant account. They bundle multiple payment methods under a single platform, streamlining the setup process. This option is often preferred by smaller businesses due to its ease of use.
Regardless of your chosen method, ensure your integration adheres to PCI DSS standards for secure data handling.

